If you’re new or just learning more about the cannabis world, you’ve probably heard some unfamiliar terminologies that piqued your interest. The two terms often thrown out in most cannabis-related posts online are cannabinoids and terpenes.
Both cannabinoids and terpenes are different compounds found in the cannabis plant. However, most people tend to confuse the two from each other. To clear out the confusion, this feature post takes a closer look at the difference between these two cannabis compounds, their origins, and how they affect the human body upon consumption.
Continue reading to learn more.
Defining Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids are generally classified into two categories:
- Endocannabinoids are cannabinoids created by the human body; and
- Phytocannabinoids are cannabinoids produced by plants, including cannabis.
Yet for this post, phytocannabinoids will be the focus.
Cannabinoids exist in several plants but are found in higher concentrations in the cannabis plant. It directly interacts with your body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS), which is responsible for regulating and balancing key bodily functions including sleep, memory, mood, fertility and reproduction, and appetite. Research has a high interest in cannabinoids because of the way they influence your ECS.
In general, the cannabis plant features over a hundred cannabinoids. Some of the popular ones include:
- Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC);
- Cannabidiol (CBD);
- Cannabinol (CBN);
- Cannabichromene (CBC);
- Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV); and
- Cannabigerol (CBG).
Defining Terpenes
Terpene is a compound found in almost all plants but is made famous by the cannabis plant. This organic compound is primarily responsible for most flora’s scent, flavor, and even color profiles. For instance, terpenes are responsible for the calming aroma of lavender or the citrusy smell and flavor of orange.
In terms of cannabis plants, terpenes are what make certain cannabis strains taste or smell different from others. If you want to learn more about cannabis terpenes, click here for more details.
The original purpose of terpenes has something to do with survivability and adaptability. Plants secrete terpenes to help deter predators or lure potential pollinators. Some terpenes can also help in a plant’s oxygenation and regenerating abilities.
The cannabis plant may also contain a hundred of known terpenes. Some of them include:
- Limonene;
- Myrcene;
- Linalool;
- Pinene;
- Humulene;
- Terpinolene; and
Cannabinoids Vs. Terpenes: How Do They Work
Cannabinoids and terpenes vary in how they act and the effect they cause. Take a closer look at how they interact with your body below.
How Do Cannabinoids Interact With The Human Body
To understand how cannabinoids work, it’s best to know ECS first. The ECS has two primary receptors:
- CB1: These are receptors found in your central nervous system; and
- CB2: These are receptors located primarily in your immune system.
Both types of receptors help in regulating homeostasis or balance. As mentioned before, cannabinoids directly bind to receptors in your ECS. Each cannabinoid binds to a receptor differently and creates unique effects.
For example, the cannabinoid THC binds to both receptors but has more affinity towards the CB1 receptor. THC, when binding with CB1 can alter serotonin levels which produce the popular ‘high’ people get from marijuana.
Meanwhile, another popular cannabinoid, CBD, can interact with both receptors but doesn’t directly stimulate your CB1 receptor, so they don’t have a psychoactive influence.
How Do Terpenes Interact With The Human Body
The effect of terpenes on the human body depends mostly on how it’s applied–orally, inhaled, or topically. Nevertheless, terpenes are best known for their aromatherapy benefits.
Terpenes stimulate your gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors. Found mostly in your limbic system, which is the area of the brain where emotional memories and personal feelings are stored and generated. It can also activate your transient receptor potential (TRP) channels which play a critical role in sensory systems including smell, vision, touch, and hearing.
Since most terpenes don’t bind to ECS receptors, they don’t have any psychoactive abilities like cannabinoids. They can shift the balance of neurotransmitters and influence your mood, but they can’t alter your perception the way cannabinoids can.
That said, some terpenes do have powerful psychoactive abilities. For example, the diviner’s sage contains the terpenes salvinorin A, which induces high mood changes and even paranoia and delirium when ingested in moderate amounts.
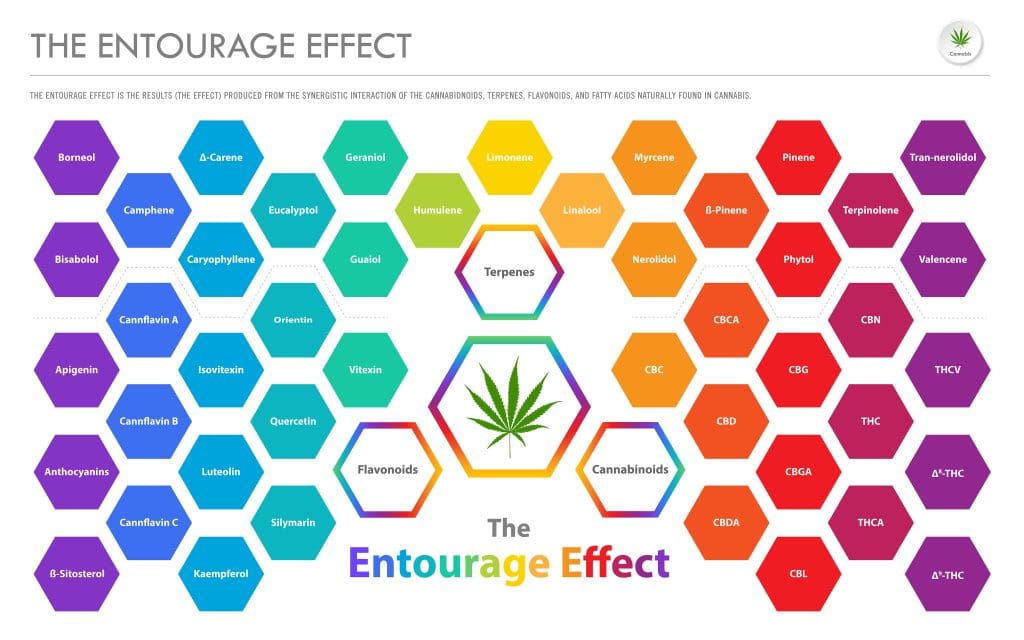
Combining Cannabinoids And Terpenes
When cannabinoids and terpenes are combined and used in the human body, they create a synergistic effect. This effect is known in cannabis as the ‘entourage effect.’ To put it simply, the entourage effect is created when the two compounds work together within your ECS to enhance each other’s therapeutic properties while tempering potential side effects.
Take Away
Both cannabinoids and terpenes are abundant in the cannabis plant. They work together to provide stronger therapeutic effects. Yet they’re completely unrelated and differ in many ways, primarily in how they affect your body.
To recap, cannabinoids are mostly found in cannabis plants. It modulates your endocannabinoid system and is mainly responsible for the therapeutic effect of cannabis. Meanwhile, terpenes, found in almost every plant, give plants their unique flavor and scent. They don’t affect your receptors as cannabinoids can, but they help in enhancing the properties of cannabinoids.






